
SEO is one of the most-used (and most important) website optimization strategies.
However, great content, backlinks, and meta descriptions won’t help much if you don’t optimize your website performance. If visitors land on your site and find it takes too long to load, or images don’t display correctly, they’re likely to choose a competitor.
That’s why improving your website performance is crucial.
What does optimizing your site look like and how do you go about it? Here’s a step-by-step guide to get you started.
What Is Website Performance?
In digital marketing, website performance generally refers to how fast a web page loads and displays content. It’s all part of visitors’ experience and it’s key to online success.
Website performance can also be used more generally, to refer to the overall impact a website has on a business. However, when digital marketers talk about website performance, we’re usually talking about how fast a site loads.
Website performance can be measured by the number of server errors, and the size of downloaded web pages. It might also be called page load time.
Website performance and page speed are imperative for any online business. A slow website can lead to:
- shopping cart abandonment
- lost conversions
- dissatisfied customers
- damage to your brand’s reputation
- lower ranking in the SERPs
No one wants any of that for their business.
Just how long does the average customer wait for a page to load? Not long.
Most sources say a website should load within two seconds. Anything longer and you risk losing not just traffic but customers.
Before you get started, it’s probably a good idea to know where you’re starting from. Google has a tool to help you out, while Uptrends also has a free speed test.

These are easy to use and provide a list of steps you can take to improve your website performance. But why should you care?
Why Is Website Performance Important?
I’ve touched on the importance of website performance in the intro, but let’s delve further. A fast responding site has many advantages, such as:
- Better user experience: Your website needs to be fast if you don’t want frustrated customers to leave.
- Higher rankings: Google PageSpeed Index rewards faster websites by ranking them higher in search results.
- Customer loyalty: The easier it is for customers to buy, the more likely they are to stay loyal.
- Improved conversion rates: Website performance can impact conversion rates because slower load times result in higher abandonment rates.
- Better mobile traffic: Your mobile visitor wants rapid results. If the mobile website performance is poor, there’s a good chance you won’t see them again.
What Affects Website Performance and How to Improve It
Several factors can affect website performance. For example, image sizes and page weight can impact speed.
Then there are some of the less obvious issues, like geographical areas.
Some of these problems might sound like huge issues, but they’re not. Most have easy fixes and I’ll walk you through the steps.
1. How Image Sizes Affect Website Performance
Images are one of the most important factors for website performance.
The reason is pretty simple: the larger your images are, the heavier your page weight is, and the longer your site takes to load.
When you optimize your website images, significant areas of your site’s performance like loading times and user experience can improve, too.
As for optimal image sizes, this varies, from picture to picture. For some guidance, try this website image size cheat sheet from Strikingly.
Here are image guidelines to help improve your website performance.
- Crop images so they don’t exceed the boundaries of the screen.
- Use images sparingly. The fewer images on a page, the quicker it loads.
- Download a page ruler to get precise dimensions.
- Use image compressions tools and plugins.
However, don’t just focus on image size, look at areas like:
- formatting
- resolution
- dimension
- quality
It sounds like a lot to consider, but it just means minimizing pictures while ensuring image size doesn’t negatively affect UI.
2. How Website Performance Is Affected by the Web Page Weight/Size
Page weight refers to page size. This covers aspects like style sheets, documents, images.
Page weight is vital for website performance because it can affect how quickly web pages load on a user’s screen. The more content included on a page, the larger it is in terms of bytes.
Stats show page weight is increasing, which can make it hard to have a fast-loading website.
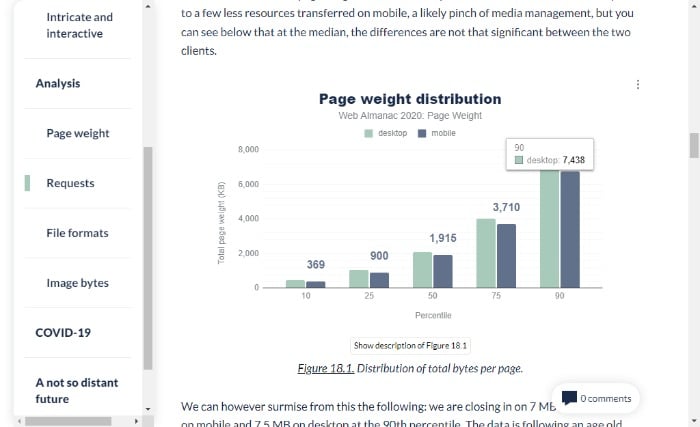
If you’re wondering what the ideal page size is, website performance expert, Tammy Everts, suggests suggests 1MB.
Not sure of your page weight? Try searchenginereport.net’s page size checker.
Now it’s time to start working on reducing your page weight.
Many of the tips in this article, like optimizing images and limiting HTTP requests, will lower your page weight. To further improve website performance, you can:
- check for any unnecessary plugins on your site
- analyze which assets are weighing down your pages
- use offsite video hosting
- combine CSS and JavaScript
- reduce the number of requests from your browser by combining multiple assets into one file
3. Reduce Redirects and HTTP Requests to Improve Website Performance
HTTP requests are a fundamental building block of the web. They allow a web browser to request information from a server and display it on a webpage.
They work like this:
When you visit a website, your browser sends an HTTP request to the site’s server, asking for data. The server sends back the information your browser needs to display the page, including HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and images.
For your page to load quickly, there should be as few HTTP requests as possible from the server to the browser.
There are several ways to reduce HTTP requests on your site, including:
- reducing image size by optimizing images with tools like TinyPNG
- optimizing JavaScript and CSS files
- merging multiple JS files
- using a Content Distribution Network (CDN)
Redirects are another issue that can slow website performance.
These redirects take users from one page to another. If a website has too many redirects or some of them point to pages that don’t exist, the website can rank lower and it may also be slower.
There are a few ways to reduce redirects on a website:
- Implement a 301 permanent redirect. A 301 permanent redirect is when you tell Google that you want this new page to replace the old one and direct traffic there.
- Add canonical tags to manage duplicate content.
- Remove old redirects.
- Use tools like Gifts of Speed to check broken links.
4. Overcome Geographical Location Limitations
You may not consider geographical location as an issue. However, the closer the two parties are, the faster the loading time.
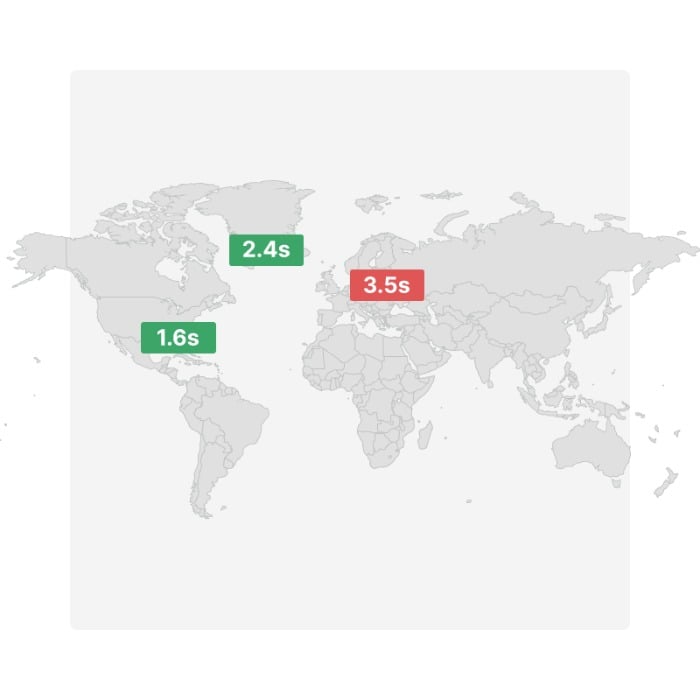
While you can’t do much about the distance between visitors to your website, you may be able to speed things up by introducing a CDN.
A CDN is a geographically distributed group of servers deployed in multiple data centers, providing content for one or more websites or web applications.
Popular CDN’s include: Rackspace, Amazon CloudFront, and Microsoft Azure.
By storing your files closer to your audience, you can reduce load time.
5. Look at Your Hosting Plan
The website hosting plan you chose years ago may have been the perfect fit, but as your site gains attention and traffic increases, it might not serve you so well anymore.
The result? A lot of downtime, a decline in website performance, and frustration for you and your visitors.
What do you do? Upgrade to a plan that suits your growing audience. If you’re using a shared hosting plan, look at some alternatives like:
- Dedicated website servers: These provide a fast and reliable connection to the web and can be scalable to meet high traffic and bandwidth needs. They’re more expensive than shared hosting, but they offer better performance for your site. This is because you get an entire server of resources dedicated to one website.
- VPS Hosting: In a nutshell, a VPS hosting solution is an affordable and scalable way to host a website. It’s a practical way for small businesses or startups with the flexibility of scaling with them as you grow.
- Serverless websites: Or a static website. These reduce load times and increase security. There are some drawbacks, so make sure to research this option before diving in.
5. Use Browser Caching
The browser cache is a temporary storage area that allows the browser to reuse content files, such as images and scripts, to reduce network traffic.
Using browser cache has a huge impact on website performance because it can save time and bandwidth, enhance the user experience, and increase loading times.
You can use some plugins to create a cache using WordPress. For non-WordPress users, here’s Google’s tutorial.
6. Render Blocking Your CSS and JavaScript.
Render blocking causes a significant slowdown in page loading time.
This is because the browser has to wait for the page to finish rendering before downloading and executing any scripts included on the page, such as JavaScript and CSS files.
Naturally, the more render-blocking elements a webpage has, the longer it takes for a web browser to load.
Don’t panic. It’s not nearly as complicated as it sounds.
You can find some easy fixes for WordPress render-blocking and Google also has some advice.
7. Other Steps to Improve Website Performance
The above sections cover the main issues that impact website performance, but there are other areas to consider, such as:
- cleaning up unclean code
- reducing excessive Flash content
- minifying your HTML
- choosing mobile-friendly, fast-loading themes
- using Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) to reduce bounce rates and increase page rankings
- fixing broken links
- compressing your files with gzip
Frequently Asked Questions About Website Performance
How do you measure the performance of a website?
There are plenty of free tools to measure your page loading times, such as Google’s PageSpeed Insights. However, if you want to measure overall performance, pay attention to KPIs like customer satisfaction and conversion rates.
What tools do you need to measure website performance?
Google Analytics provides a set of tools to monitor website performance, including Site Speed, Pages per visit, Bounce Rate, and Conversion Rate.
Pingdom and GTmetrix measure your site speed, and Uptrends provides a comprehensive set of testing tools, and a free speed test.
How long does it take to analyze website performance?
You can complete loading time tests in seconds, and you should analyze them at regular periods throughout the year. In addition to speed, other areas of website performance to measure are your content, on-site behavior, and user acquisition metrics.
What is a good website performance?
The best-performing sites load within two seconds, and that’s what you should aim for.
Conclusion: Website Performance
There is more to a website than SEO, great content, and good-looking images. Whether you’re an ecommerce site, blog, or website owner, website performance is crucial to online success.
Great website performance makes it easier to rank and helps keep traffic on your website.
It also enhances SEO, helping to keep your website at the top of rankings and potentially increasing your overall conversions.
Enhancing your website performance might sound complex, but it’s pretty simple. Start by reducing your image sizes, limiting page weight, and upgrading your web host package.
Do you have tips to improve website performance? Share them below.
from Blog – Neil Patel https://ift.tt/3F4DPAl
via IFTTT
No comments:
Post a Comment