
Let’s talk about BERT. No, not Bert and Ernie, but the Google Update.
What is it, why does it matter, and what do you need to do?
Well, Google BERT was actually a pretty big update that impacted 1 in 10 search queries.
Before we go into how it impacts SEO, let’s cover what this update is all about.
So, What Was Google’s BERT Update?
Bert stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers.
What the heck does that mean, right?
Google, in essence, adjusted its algorithm to better understand natural language processing.
For example, if you put your flight number into Google, it shows you the flight status. Or a calculator may come up when you type in a math equation. Or if you put a stock symbol in, you’ll get a stock chart.
Or a simpler example is when you start typing into Google, its autocomplete feature figures out what you are searching for before you even finishing typing it in.
But Google has already had all of that figured out before BERT. So let’s look at some examples of Bert in action.
Examples of Google BERT in Search Results
Let’s say you search for “brazil traveler to usa need visa”.
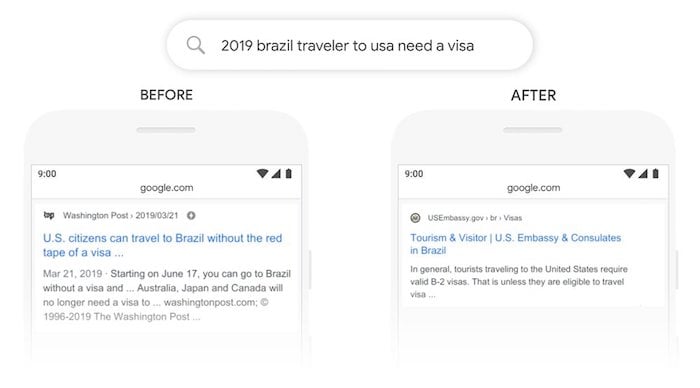
Before BERT, the top result would be how US citizens can travel to Brazil without a visa. But look at the search query carefully–it’s a small difference but it has a huge impact.
The search wasn’t about US people going to Brazil, it was about people from Brazil traveling to the US.
The result after the BERT update is much more relevant.
Google is now taking into account prepositions like “for” or “to” that can have a lot of meanings to the search query.
Here’s another example… “do estheticians stand a lot at work”…
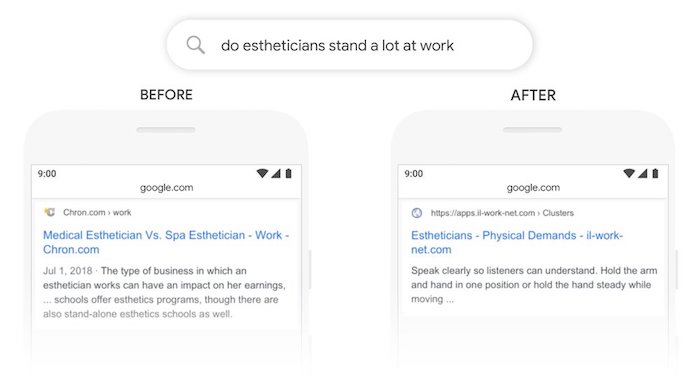
Google used to previously match terms. For example, their system used to think “stand” is the same as “stand-alone”.
Now they understand that the word “stand” has the context of physical demand. In other words, is the job exhausting and do you have to be on your feet a lot?
One more, “can you get medicine for someone pharmacy” …
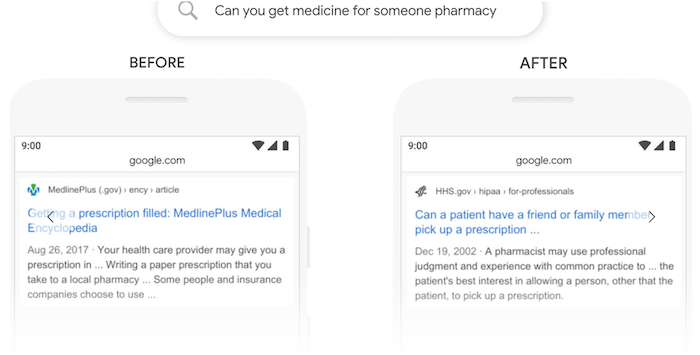
As you can see from the before and after picture, it’s clear that the new result is more relevant.
Same with this one on “math practice books for adults” …
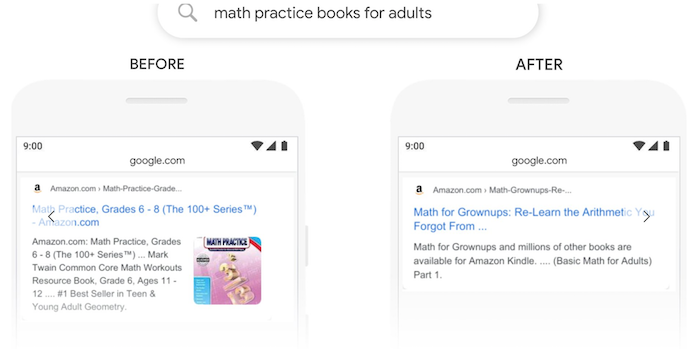
What Other Changes Did Google BERT Bring?
Google also changed featured snippets when BERT rolled out.
For example, if you searched for “parking on a hill with no curb,” Google used to place too much emphasis on the word “curb” and not enough emphasis on the word “no.”
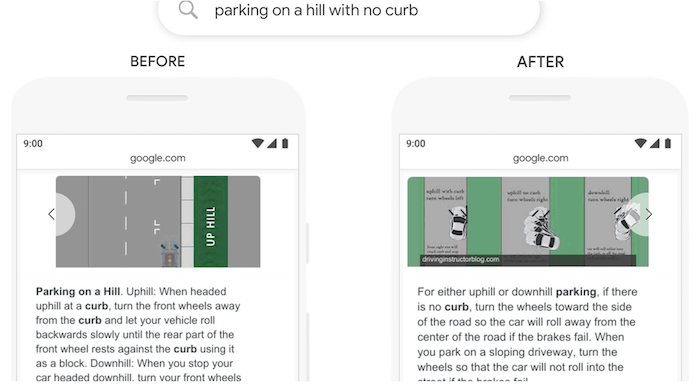
That’s a big difference.
How to Tell if Google BERT Impacted Your Site
Did you notice a drop in traffic after BERT?
Log into Search Console, click on “search results,” and click on the date button.
Then click on compare and select the dates where your traffic dropped and compare it to the period before BERT went live in October 2019.
Then select “Queries” and sort by the biggest difference.
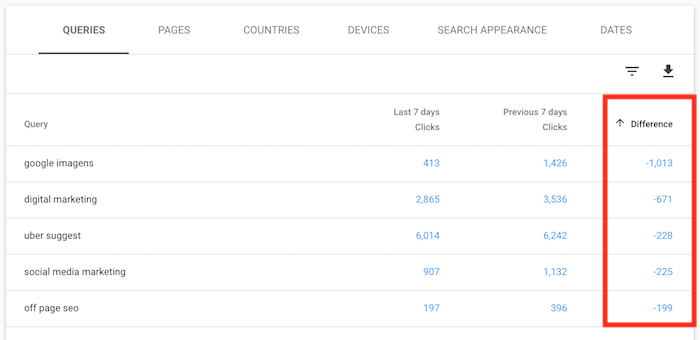
You’ll have to dig for the longer-term search queries as those are the easiest to fix. And if you are unsure about what to fix, just search for the terms on Google that dropped and look at the top-ranking competitors.
Comparing their page with yours as it will provide some insights.
How Google BERT Impacts Content Marketing
The BERT update made search results much more relevant for searchers and it created a better experience for everyone who uses Google.
But how does BERT affect your content marketing strategy? Here’s a few things you need to know about the impact of Google BERT update.
1. Google BERT Impacts Top-of-the-Funnel Terms
BERT mainly impacts top-of-the-funnel keywords, which are informational-related keywords.
As you may know, there are main types of search queries:
- Informational
- Navigational
- Transactional
An informational query is like someone looking to lose weight. They aren’t sure how so they may search for “how to lose weight”.
Once they perform the search, they may find a solution, such as different diets. From there they may search for a solution, using a navigational query such as “Atkins diet”.
Once someone figures out the exact solution, they then may perform a transactional search query, such as “the Atkins diet cookbook”.
If you want to not just maintain your rankings but gobble up the rankings of your competition, you’ll want to get very specific with your content.
Typically, when you create content, which is the easiest way to rank for informational related keywords, SEOs tell you to create super long content.
2. Focus on Quality, Not Length of Content
Yes, you may see that a lot of longer-form content ranks well on Google, but their algorithm doesn’t focus on word count, it focuses on quality.
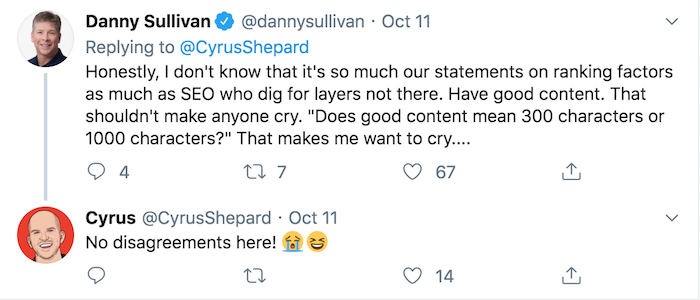
The context of the tweet from Danny Sullivan, who is Google’s search liaison, is that he wants SEOs to focus on creating content that is fundamentally great, unique, useful, and compelling.
So when you use tools like Ubersuggest to find new topics to go after, you need to make sure your content is super-specific.
For example, if you have a business about fitness and you blog about “how to lose weight without taking pills”, your content shouldn’t focus on diet shakes or supplements or anything similar to diet pills. Instead, it should discuss all of the alternative diet methods.
BERT helps Google better understand what people are really looking for, so SEOs should focus on creating great content, not looking for a magic optimization key.
3. Stop Worrying About Keyword Density
Yes, a lot of SEOs have moved away from this, but I still get a handful of emails each day asking me about keyword density.
Keyword density is even less important after BERT as Google better understands the context of the content you are writing.
4. Long-Term Keywords Matter More than Ever
BERT (and changes like Passage Indexing) make it easier than ever for Google to understand the context of a page. Which means long-tail keywords are critical.
They help Google (and users) better understand what your page is actually about.
Google BERT Content Marketing Opportunities
So, how do you make the most of BERT and other AI Google updates? Here are a few strategies to implement.
Create Highly Specific Content
To make the most of BERT, you need to create highly specific content around a topic.
It’s not necessarily about creating a really long page that talks about 50 different things that’s 10,000 words long. It’s more about answering a searcher’s question as quick as possible and providing as much value compared to the competition.
Just like when you search for “what is it like to be in the Olympics,” you’ll see a list of results that look something like this:
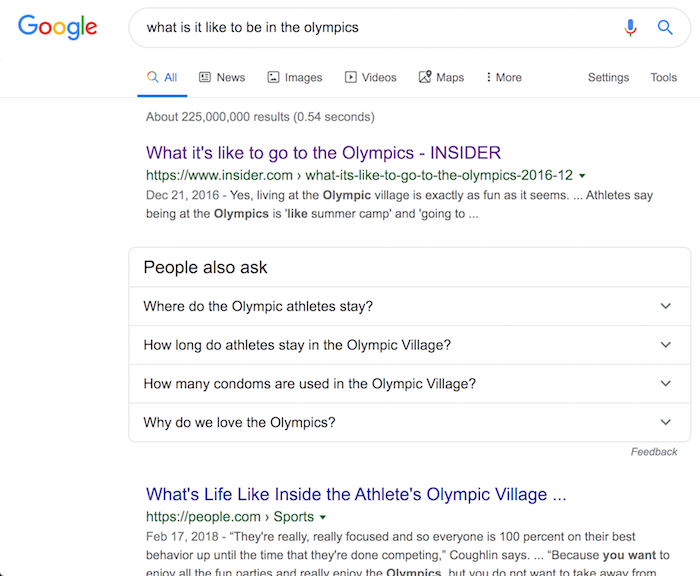
Although the first result has the title of “What it’s like to go to the Olympics”, the article doesn’t break down what it is like to go as an attendee, it breaks down what it is like to go as an athlete. Just like a searcher would expect based on the query.
BERT was clearly able to figure this out, even though the title could have gone either way. The article itself isn’t that long: it only has 311 words.
If you want to do well when it comes to ranking for informational keywords, go very specific and answer the question better than your competitors. From videos and images to audio, do whatever needs to be done to create a better experience.
Focus on Long-Tail Keyterms
Does BERT mean long form content doesn’t work any more?
Not at all. It’s just that every SEO already focuses on long-form content. They are going after generic head terms that can be interpreted in 100 different ways and that’s why the content may be long and thorough.
In other words, focus more on long-tail terms.
It might seem obvious, but lets look at the data.
It all starts with Ubersuggest. If you haven’t used it yet, you can type in a keyword like “marketing” and shows you the search volume and gives you thousands (if not millions) of keyword variations.
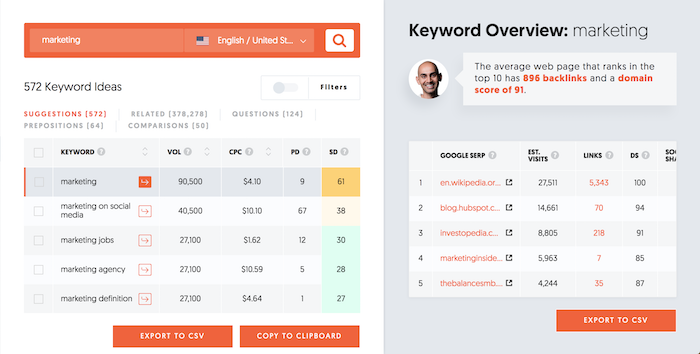
In the last 30 days, 4,721,534 keyword queries were performed on Ubersuggest by 694,284 marketers. Those 4,721,534 searches returned 1,674,841,398 keyword recommendations.
Sure, SEOs could type in head terms to find more long-tail phrases, but when we look at what keywords people are selecting within Ubersuggest and exporting, 84% of marketers are focusing on 1 or 2-word search terms.
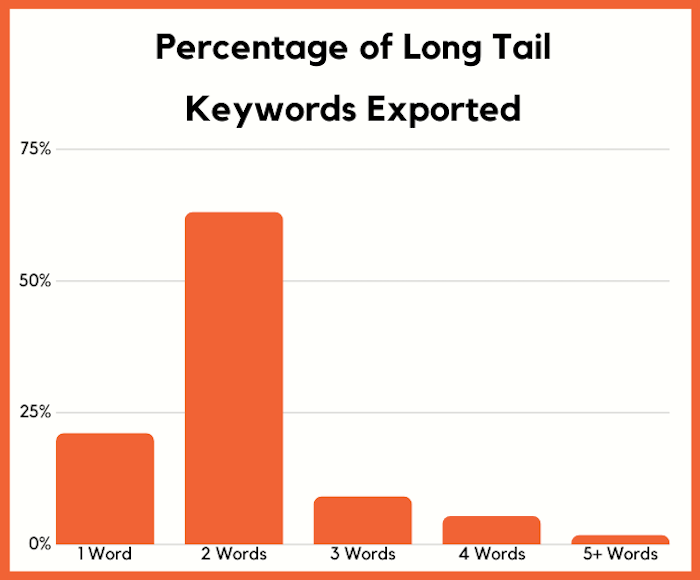
Only 1.7% of marketers are focusing on search terms that are five or words longer.
Following the strategy of creating content around very specific long-tail phrases is so effective that sites like Quora are generate 60,428,999 visitors a month just from Google alone in the United States.
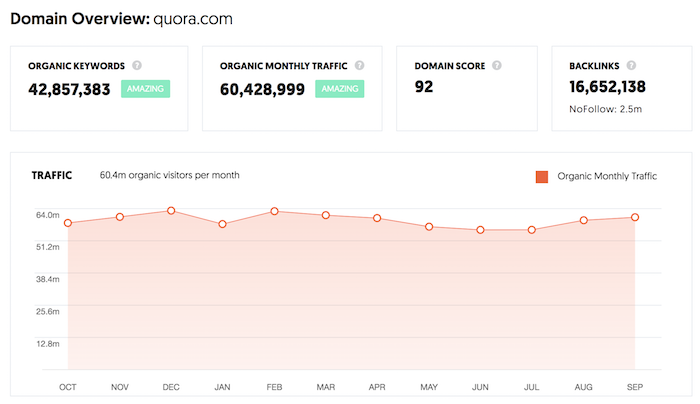
And a lot of their content isn’t super detailed with 10,000-word responses. They just focus on answering very specific questions that people have.
Conclusion
Even if Google BERT impacted your traffic or rankings, it is a good thing.
I know that sounds crazy, but think of it this way–if someone searched for “how to lose weight without diet pills” and they landed on your article about how diet pills are amazing, they are just going to hit the back button and go back to Google.
In other words, it is unlikely that the traffic converted into a conversion.
Sure, you may lose some traffic from this update, but that traffic was ruining your user metrics and increasing your bounce rate.
Plus, this is your opportunity to create content that is super-specific. If you lost traffic, look at the pages that dropped, the search queries that you aren’t ranking for anymore, and adjust your content or create new content that answers the questions people are looking for.
So, what do you think about BERT? Did it impact your site when it first rolled out?
The post A Refresher on How the Google BERT Update Affects Content Marketing appeared first on Neil Patel.
from Blog – Neil Patel https://ift.tt/2Wo19El
via IFTTT
No comments:
Post a Comment